

Although some users such as radio amateurs often require long distance radio communications and can accommodate linking with others anywhere on the globe.įor other users such as broadcasters and some diplomatic radio communications, specific target areas may be needed. The skip distance is dependent upon a variety of different factors. However for some applications where a specific target area is required, the angle of radiation can be tailored so that the required target region is covered in conjunction with the specific ionospheric region. This means that radio communications links can cover greater distances if low angles of radiation are used. A lower angle of radiation will lead to longer skip distances as a result of the geometry.

The skip distance is the distance over the Earth's surface between the point where a radio signal is transmitted, and the point where it is received having travelled to the ionosphere, and been refracted back by the ionosphere. Skywaves travel towards the ionosphere Skip distance The angle between the line of the skywave signal and the Earth’s surface at that point may be shallow or steep. Unlike a ground wave it does not follow the contour of the ground, but instead it is directed towards the ionosphere. The skywave refers to the signal that travels away from the Earth’s surface towards the ionosphere. They have an impact on aspects of radio communications links including the times and frequencies chosen, the antennas used, the transmitters and receivers employed and a variety of other aspects. In order to cover large distances using ionospheric radio propagation the concepts of skywaves, skip distance and skip zone are important. Skywaves, skip zone and skip distances are three key concepts show why radio communications signals are heard in some places and not others. Understanding the way in which HF radio signals actually propagate can help the effects of ionospheric propagation to be used to its best.
Antenna and wave propagation ppt download how to#
Ionospheric propagation Ionosphere Ionospheric layers Skywaves & skip Critical frequency, MUF, LUF & OWF How to use ionospheric propagation Multiple reflections & hops Ionospheric absorption Signal fading Solar indices Propagation software NVIS Transequatorial propagation Grey line propagation Sporadic E Spread F
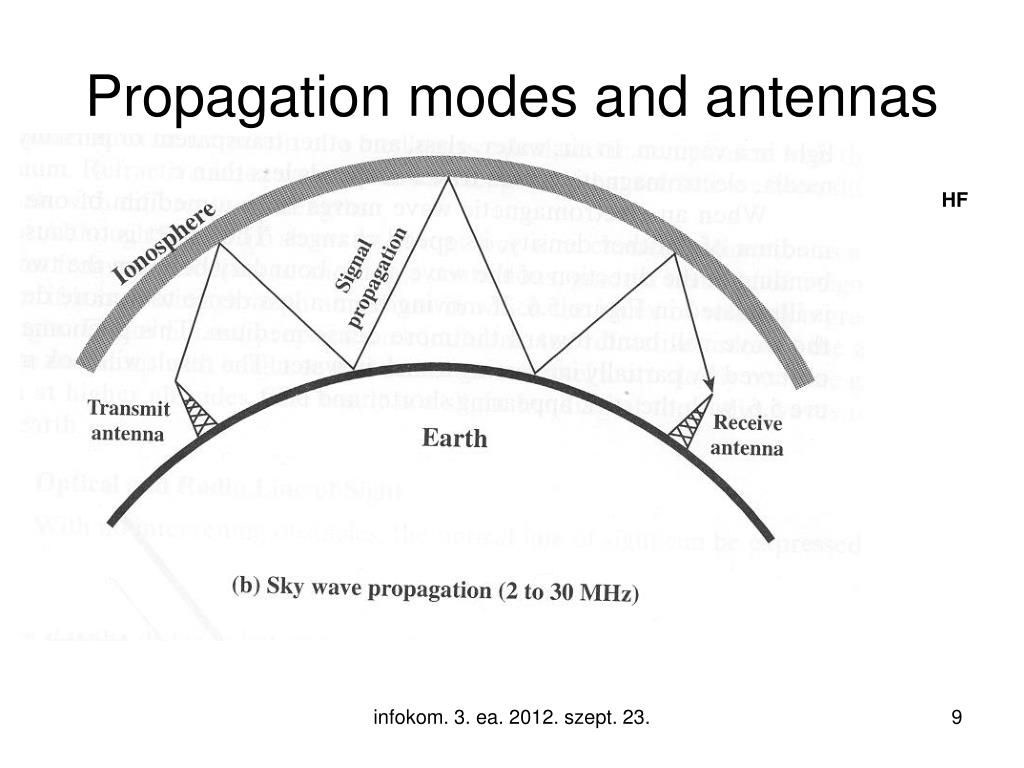
Ionospheric propagation tutorial includes. Skywaves Skip Distance & Skip Zone Three key topics within ionospheric HF propagation and radio communications are skywaves, skip distance and skip zone.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
